Testosterone, Mortality and Longevity
- Published in Testosterone Replacement Therapy

Population studies show that men with low or low-normal testosterone levels are at an increased risk of mortality compared to those with higher levels, and that cardiovascular disease accounts for the greater proportion of deaths in men with low testosterone.[1]
Here I summarize a medical review paper which addressed the following two questions: [1]
1. Is testosterone deficiency directly involved in the pathogenesis of these conditions or is it merely a biomarker of ill health and the severity of underlying disease processes?
2. Does testosterone replacement therapy retard disease progression and ultimately enhance the clinical prognosis and survival?
Testing for testosterone deficiency - things to know about the blood draw
- Published in Testosterone Replacement Therapy
The first step (aside from identifying symptoms) in diagnosing testosterone deficiency, aka low-T, is to do a blood test.
Here I cover some important practical things to know about a blood draw for testosterone analysis...
Testosterone and Fat Loss - the Evidence
- Published in Testosterone Replacement Therapy
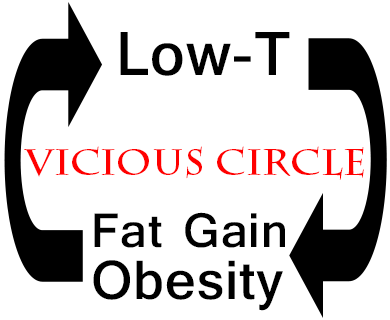
It is well documented that obesity may cause hypogonadism, and that hypogonadism may cause obesity [1-4] This has generated debate about what condition comes first; obesity or hypogonadism? And what should be the first point of intervention?
In this article I will summarize data from several reviews on the associations of hypogonadism and obesity [1-4], and make the case that these conditions create a self-perpetuating vicious circle. Once a vicious circle has been established, it doesn’t matter where one intervenes; one can either treat the obese condition or treat hypogonadism first. The critical issue is to break the vicious circle as soon as possible before irreversible health damage arises.
Nevertheless, as I will explain here, treating hypogonadism first with testosterone replacement therapy may prove to be a more effective strategy because it to a large extent “automatically” takes care of the excess body fat and metabolic derangements. In addition, treating hypogonadism first also confers psychological benefits that will help obese men become and stay more physically active.
How well informed are general practitioners and cardiologists about testosterone deficiency and its consequences?
- Published in Testosterone - Men

A rapidly growing body of medical research is showing that testosterone deficiency (aka hypogonadism and low-T) is strongly associated with a wide range of detrimental health outcomes [1, 2], and that testosterone replacement therapy improves those health parameters that are negatively affected by testosterone deficiency.[2, 3]
Therefore, leading testosterone scientists now view testosterone deficiency as a cardiovascular risk factor that contributes to the development of cardiovascular disease.[4-7]
As general practitioners and cardiologists primarily care for these patients with cardiovascular disease, a survey study was conducted to assess their knowledge, beliefs and clinical practice with respect to testosterone deficiency and cardiovascular health.[8]
Testosterone Boosting Medications and Cardiovascular Risk - a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Published in Testosterone Replacement Therapy
Accumulating evidence shows beneficial effect of testosterone therapy on a wide range of health outcomes, including inflammation, insulin sensitivity, muscle mass, body fat mass, lipid profiles, endothelial, bone mineral density, energy and vitality, mood, sexual function and overall quality of life. [1-9]
Despite this, concerns have been raised that testosterone therapy could have detrimental effects on cardiovascular disease.
In this article I summarize results from a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis, the largest to date, of all placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials (RCTs) on the effect of testosterone therapy on cardiovascular-related outcomes.[10]
Incidence of Prostate Cancer after Testosterone Therapy for up to 17 years
- Published in Testosterone Replacement Therapy
One of the major concerns among doctors and patients with testosterone therapy is its allegedly negative effect on the prostate.[1] However, according to the current ISA, ISSAM, EAU, EAA, ASA clinical guidelines, there is no conclusive evidence that testosterone therapy increases the risk of prostate cancer or benign prostatic hyperplasia.[2]
The guidelines also state that there is also no evidence that testosterone treatment will convert subclinical prostate cancer to clinically detectable prostate cancer.[2]
Despite this, many men are being denied testosterone therapy because of undue fears that it would cause harm to the prostate. Here I summarize the results from a study that investigated incidence of prostate cancer with testosterone therapy for up to 17 years.[3]
Adherence to testosterone therapy - short term treatment is not sufficient for achievement of maximal benefits
- Published in Testosterone Replacement Therapy

Testosterone therapy confers a wide range of health benefits for hypogonadal men, including improvements in body composition (reduction in body fat, increase in muscle mass), lipid profile cardiovascular function, insulin sensitivity/glucose metabolism, bone mineral density, inflammatory parameters, quality of life and longevity.[1]
Despite this, there is a high discontinuation rate with testosterone therapy.[2, 3]
In this article I summarize results from two studies that investigated adherence to testosterone therapy and treatment patterns.[2, 3]
Efficacy and safety of injectable testosterone undecanoate (Aveed or Nebido) for the treatment of hypogonadism
- Published in Testosterone Replacement Therapy

Since its approval in 2004, many clinical studies have been conducted with testosterone undecanoate, the first long-acting injectable form of testosterone.
Testosterone undecanoate has been proven to have an excellent safety profile and need only be administered four times annually to produce stable testosterone levels.[1]
Long-term studies have validated the clinical efficacy of testosterone undecanoate in maintaining stable therapeutic levels of testosterone and safely conferring the desired benefits of androgen replacement.[1]
Here I summarize the results from a comprehensive meta-analysis of all uncontrolled and placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials (RCTs) demonstrating the effect of injectable testosterone undecanoate on multiple clinical outcomes.[2]
Testosterone Levels, Testosterone Therapy and Cardiovascular Risk in Men
- Published in Testosterone Replacement Therapy

Hypogonadism, also known as testosterone deficiency, is increasing in prevalence worldwide. While a rapidly expanding body of research is documenting the detrimental health consequences of hypogonadism, at the same time there is a prevailing concern and misunderstanding about the effects of testosterone therapy on cardiovascular risk.
In this article I present a summary of a recently published comprehensive review on the association of hypogonadism with cardiovascular risk factors, and the effect of testosterone therapy on those risk factors.[1]
Testosterone Deficiency - Prevalence and Treatment Rates
- Published in Testosterone Replacement Therapy
Testosterone deficiency, also known as hypogonadism, is gaining recognition among both clinicians and the general population. This article summarizes the findings from a review on the prevalence of testosterone deficiency, as well as the proportion of hypogonadal men who are receiving testosterone treatment.[1]
While testosterone prescribing has increased lately, as you will find out here, the prevalence of testosterone deficiency far exceeds the prescribing rate; i.e. majority of men with low-T are still not being treated with testosterone therapy.
You may be surprised to find out that testosterone deficiency is still not well-understood by general practitioners and cardiologists, and that these key clinicians lack knowledge on its deleterious cardiovascular effects. Therefore, even man needs to take control of his own health and don't let any ignorant or old-school doctor deny you a prescription that you may need...



